Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In today’s digitally driven world, the question “What does a user experience designer do?” is gaining more prominence. With the growing significance of user-centered design, businesses are increasingly recognizing the pivotal role that UX designers play in shaping successful products and services. This article aims to unravel the multifaceted role of a User Experience Designer and explore the various aspects of their work .

User Experience Design (UXD) is a field that revolves around enhancing the overall experience of users when interacting with a product, service, or system. A UX Designer’s primary goal is to ensure that these interactions are not just functional but also delightful and user-friendly.
So, what exactly does a User Experience Designer do?
A User Experience Designer wears many hats, and their responsibilities can vary widely. They are expected to be versatile, often taking on tasks that span multiple domains. Let’s delve into some of the key aspects of their role:
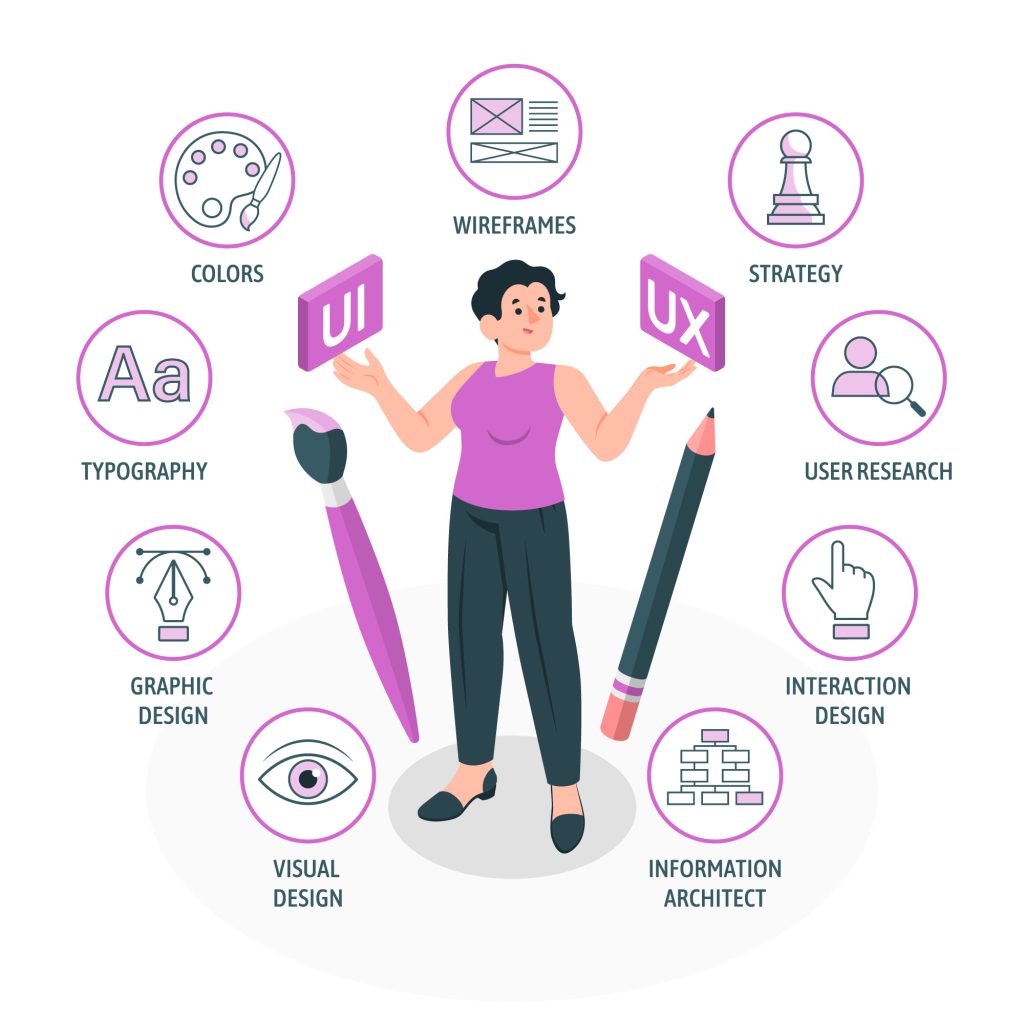
One day, a UX Designer might find themselves diving into data, akin to a number-crunching analyst. They meticulously examine user data, conduct surveys, and analyze user behavior to gain insights into user preferences and pain points. Data analysis is the foundation upon which sound design decisions are made.
On another day, a UX Designer may be crafting pixel-perfect mock-ups for the next big product release. These mock-ups serve as visual blueprints for the development team, guiding them on how the product should look and feel. Creating aesthetically pleasing and functional designs is a core part of the UX design process.
Some UX Designers have a strong inclination towards the business side of things. They play a critical role in managing the product’s lifecycle, from conceptualization to execution. They work closely with stakeholders to ensure that the product aligns with business goals and user needs.
In the ever-evolving landscape of UX design, a new trend is emerging – specialized UX designers. Many companies are moving away from the idea of having one designer do it all and are instead building well-rounded teams of designers with different skill sets and inclinations. This approach is akin to having specialists in healthcare, where you wouldn’t go to the same doctor for every ailment.
To understand the various specializations within UX design, let’s delve into the quadrant model, which categorizes UX designers into four primary quadrants. While these distinctions aren’t always clear-cut and often overlap, they provide a good starting point for understanding the diversity of roles within UX design:
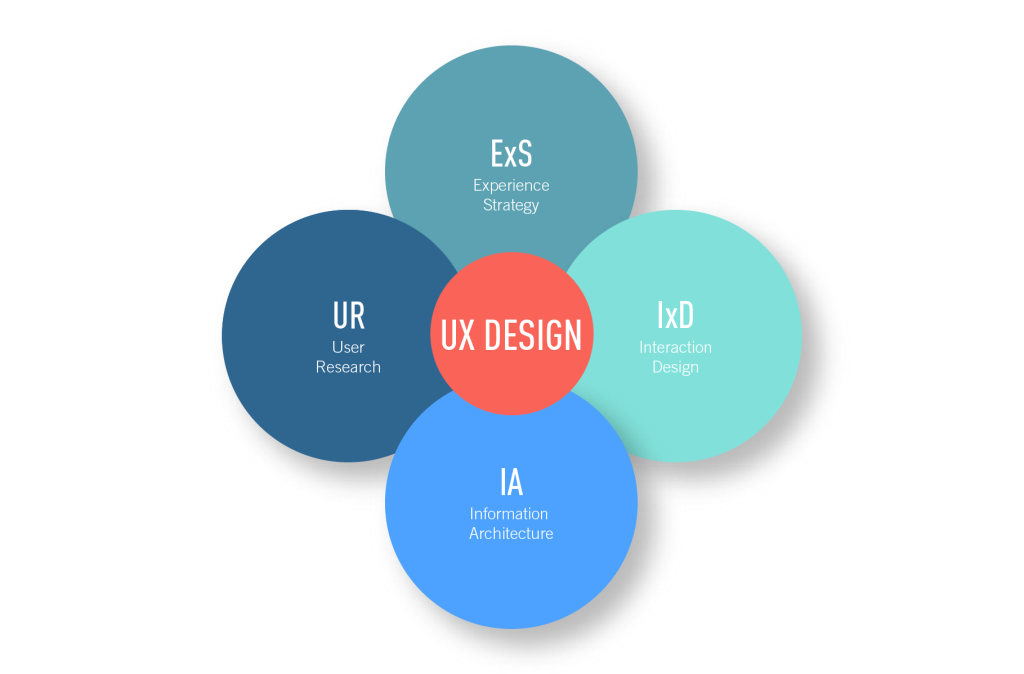
UX Designers often specialize in one or two quadrants that best align with their skills and interests. This flexibility makes UX design a captivating career choice, attracting professionals from diverse backgrounds. In this field, there’s always more to learn and explore, making it a dynamic and engaging profession.
In a world where digital experiences are at the forefront of businesses, User Experience Design remains a dynamic and ever-evolving field. UX Designers continue to innovate and adapt to emerging technologies, user behaviors, and design trends.

So, what does a User Experience Designer do? The answer is multifaceted. They are the architects of delightful digital experiences, the researchers who understand user needs, and the strategists who align design with business goals. Whether you’re drawn to strategy, interaction design, user research, or information architecture, the world of UX design offers a vibrant and continually evolving landscape to explore and excel in. As businesses increasingly prioritize user-centered design, the role of a User Experience Designer has never been more critical, and the opportunities in this field are boundless.
[…] Defining UX Design […]
[…] Understanding the Role […]